Rigid foam types
Silly question but I can’t seem to find the answer anywhere. What is the difference between the type 2 and type 3 and other types of rigid foam?
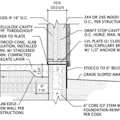
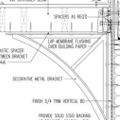
GBA Detail Library
A collection of one thousand construction details organized by climate and house part






Replies
try: https://www.greenbuildingadvisor.com/article/choosing-rigid-foam
Before talking about the numerical type you'll probably want to consider the 3 broader categories: Polyiso, XPS, and EPS.
The numerical 'type' (of which is more specific to EPS, I believe) has most to do with compressive strength and to some degree R-value and density/ water sorption characteristics. The above article covers it and links to other good info.
With EPS, the number has to do with the density of the material. Type II is heavier than Type I, for example. Type I is also crumbly and more difficult to work with as a result, it's similar to the crumbly type of styrofoam using in shipping. Type II is much more durable.
There are also related properties like compression strength as mentioned above.
For XPS, you generally see the compressive strength listed (1o PSI, 25 PSI, etc) as the primary difference. R value per inch is about the same.
For PolyISO, there are different facers (metal foil, kraft paper, etc.), and different densities per cubic foot, with the denser material (usually the foil faced stuff) having slightly higher R value per inch than the lighter (usually the kraft faced stuff) material.
Bill