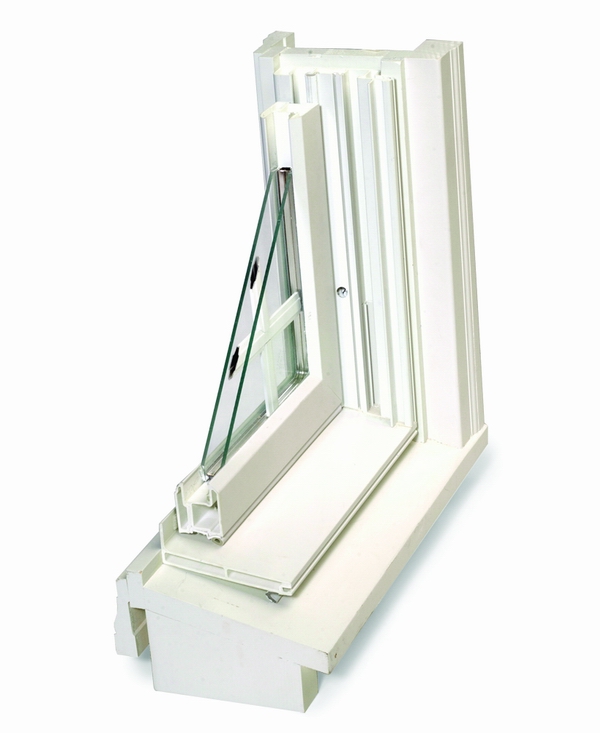

True divided-light windows lose more heat.
Heat loss is highest at the edges of window glass. True divided-light windows lose more energy than windows with internal muntins because there are many more edges where heat can escape. Simulated divided-light windows, with the muntins sandwiched between sheets of glass, retain more of the thermal performance of the larger glass size than true divided-light windows. Because National Fenestration Rating Council ratings are not based on divided-light windows, they may overstate the thermal performance of divided-light windows.
—_This GREEN BUILDING TIP is from our Strategy Generator. Build a tip sheet
for your green building or remodeling project under the Strategies & Details tab._
GREEN POINTS
LEED for Homes: Up to 3 points for high-efficiency windows.
NGBS/ICC 700: Depending on the climate zone up to 12 points for windows that meet U-value and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient maximums.
LEARN MORE
Windows: Glass, Ratings, and Installation
BROWSE THE PRODUCT GUIDE
Weekly Newsletter
Get building science and energy efficiency advice, plus special offers, in your inbox.













2 Comments
please define terms
Consumers reading this are unlikely to know what a "divided-light window" is.
Please define the terms internal muntin, and divided-light.
thanks
Definitions
Mark,
A muntin is a strip of wood or metal separating and holding panes of glass in a window sash. Each pane of glass (or each "insulated glazing unit") separated by a muntin is called a light.
Most modern windows have one light per sash. Because large pieces of glass used to be difficult (or expensive) to make, older sash often had two, four, or six small lights per sash. These multiple-light sash were said to be "divided-light sash" or sometimes "divided-light windows."
True divided light sash have small panes of glass separated by muntins. Simulated divided-light sash have one large piece of glass with applied grilles that look from a distance like muntins — to give modern windows that "old-timey" look. In some cases, these grilles are placed between two sealed pieces of glass -- these are the "internal muntins" mentioned above.
Log in or create an account to post a comment.
Sign up Log in