
The Edison Electric Institute predicts that by the year 2030, about one-third of cars (and trucks) in the U.S. will be battery powered. Environmentally, it’s an overall win that will help to reduce carbon emissions. Add in fuel cost savings and various federal and state rebates, and electric vehicles (EVs) start to look better and better to more folks. For homeowners and renters with grid-tied solar, having an EV is a no-brainer. Often the low cost of electricity makes it possible to power the car very inexpensively or for free, if the electric customer has a regular surplus of PV-generated power.
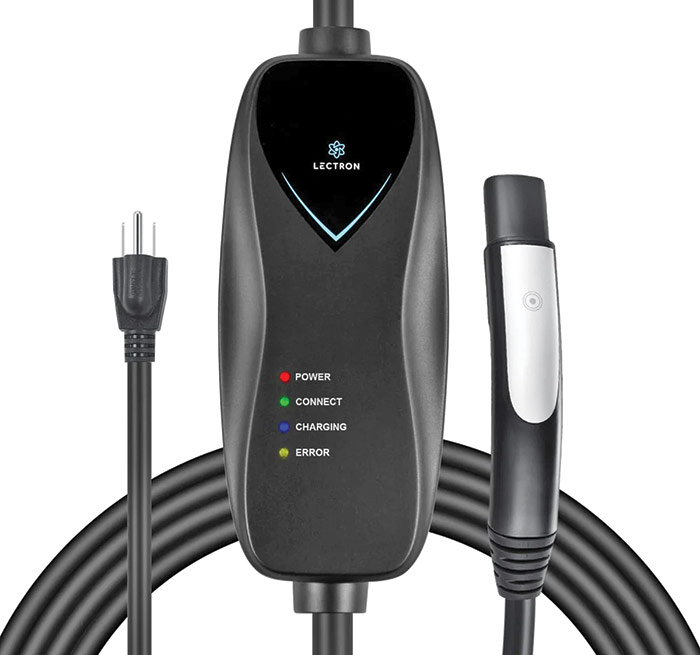
Owning a home EV charger is the least expensive and most convenient way to charge an EV battery. EV chargers, also referred to as electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), are classified by the amount of amperage they can supply to your car. The more amperage, the faster the charge.
Your car battery’s size is measured in amps or kilowatts (kw), and also has a limit of how much charge it can take over a period of time, known as its acceptance rate. Level 1 and 2 chargers supply household AC power to an EV, where an onboard device converts the AC power to DC before it’s stored in the battery. Level 3 chargers supply DC power directly to the battery, making a faster charge time possible.
3 LEVELS OF EV CHARGERS
Faster charging rates cost more

Weekly Newsletter
Get building science and energy efficiency advice, plus special offers, in your inbox.

This article is only available to GBA Prime Members
Sign up for a free trial and get instant access to this article as well as GBA’s complete library of premium articles and construction details.
Start Free TrialAlready a member? Log in














18 Comments
Bad timing on the JuiceBox shout out! They just announced they are leaving North America and taking their app with it, turning it from a "smart" charger with customization options into a dumb charger. This is why I hate hardware that requires a cloud app to manage it.
Just follow the link you posted, it will take you to the announcement.
Don't forget about Energy Management Systems!! Section 8 of the Canadian Electrical Code allows you to ignore your EV Charger, likely the largest load you will ever have in your home, when determining your panel capacity. I'm guessing the US regulations are similar. With one of these installed you almost certainly WILL have sufficient capacity in your panel, as it monitors your use and turns the car charger down or off to prevent an overload. They come in a few different flavours, for a parking garage they will divide the available power up amoung the chargers in use, for townhomes with shared electrical rooms they will monitor your home panel and the main electrical room panel to keep both safe.
@Cafferatak2
The US regulations, NFPA 70, are just starting to become aware of load management system. Like you I calculate EV load as zero. For two reasons: don't want to charge in peak hours anyway, and because I can.
No, you can't calculate it as zero and be code compliant, just based on your promise to only charge at night. But US Nat. Elec. Code (NFPA 70) has allowed load management for a while now. The 2023 code reorganized it and clarified it but it's not new.
Wallbox, Emporia and Tesla all offer that capability with an optional accessory that measures the feeder current.
Yes, zero based on EVLMS. Then for cost reasons set to zero based on a schedule.
This article is missing a few things and has some misinformation.
" Some chargers have internal GFCIs; " is not correct. None have a GFCI as defined by the NEC, but ALL have a series of protection devices including a "residual current detector". As the article stated having a GFCI in front of an EVSE is undesirable, but you may be hamstrung by locally adopted code. NEC Section 210.8(F) is under revision now in the NEC process, relating to this exact point. EVSE have an excellent safety record because they all have internal protection inherent in the design: it does not NEED a separate dumb GFCI to be safe.
A huge install issue is the heat generated by long term EV charging. Details matter, including use of not your wrist, but a calibrated tool to make connections. Loose connections make heat, which melts plastic.
Many first timers to EV charging think they need a big 30, 40 or 48 amp charger. Probably not at home. Averaged over a week even a 20 amp Level 2 charger is going to be just fine. The NEMA 6-20 outlet installs with regular #12 wire, and works great. Or hard-wire one less failure point, and a pass on expensive GFCI and the associated vampire power of a GFCI.
When I decided to install a charger, I opted not to install a plug in one because I had read about cheaper recepticals melting and robust recepticals were very expensive. I hard wired a Grizzl-E charger adjustable from 50 amps to 16 amps and it has worked very well for 18 months. Remember that under most codes, because the charging load is continuous you should use wire and recepticals for higher amps than your charger can deliver. At least a 20% cushion is required . So for instance, if you use 8 guage wire (suitable for 40 amps) the maximum amperage for the charger should not exceed 32 amps and a 30 amp breaker. I was more conservative: I used 8 guage wire, a 30 amp breaker; but set the charger at 24 amps. This was plenty fast for me since I always charge overnight.
One aspect of EV's that is rarely discussed is efficiency: miles per kilowatt (kwh). This is a key factor because the more efficient an EV, the cheaper it is to run and the longer the range for the size of the battery pack. My Ioniq 6 is perhaps the most efficent EV around. Over the last 16 months I have driven 35, 000 miles (in climate zone 5) and averaged 4.8 miles per kwh. At 10 cents a kwh I can go 48 miles for a dollar, 144 miles for the $3 price of a gallon of gas. And my 77 kwh battery can get me 370 miles of range. of course, I drive conservatively. Driving with a heavy foot and using a great deal of cabin heat (I like my great seat heaters) will reduce range considerably.
Your explanation of the 80% derating is great, but I think you have a typo: wire rated for 40 A running 32 A charging should have a 40 A breaker, not 30.
Right....you can use a 40 amp breaker with 8 guage wire.... but for additional safety I put a 30 amp breaker on-since the charger is set at a maximum 24 amps, a 30 amp breaker is sufficient and gives a little more protection from surges. If in the future I decide to increase the charger to 32 amps I can swap out to a 40 amp breaker.
Another option is to put in the fully rated breaker and wire.
But you'll have some heating losses in the wire when used at max, so don't.
Set the app to a lower value, unless you really need a fast charge.
For the few hours a year you need to set the thing to "11", the heat will be insignificant.
Hardwire is actually less expensive than plugs if you get a charger that can be hardwired.
Hardwire does not need gfci breaker in the load center if the charger is protected already.
Plug 14-50 setup needs these extra items that hardwire does not need:
- gfci breaker in the load center $75+
- industrial 14-50 plug $50+
- if installing outside, a plug bo with cover. Good luck finding one that fits the larger diameter industrial 14-50 $40+
- extra neutral conductor that is not even used by the charger $1.50/ft for #6
Plug 6-50 needs most of the above except the extra unused neutral conductor.
I would never install a non industrial 14-50 or 6-50 as there are way too many images online of melted plugs.
Yes, and hard wiring is also good for flexibility: you an hard wire a level 2 charger at any circuit capacity from 15 A to 100 A, to match the capacity you have available and your charging rate needs. (Check that the specific model you are buying can support the current you want, but many can do anything from a 20 A circuit to a 60 A circuit.)
Also, hard wiring is needed to support load management which is good for scenarios where you are up against limits of your service capacity, either now, or after you take future steps to electrify anything in your home that still uses natural gas.
Great point on plugs (recepticals). If you put an industrial grade receptical next to a cheap unit, you can see the difference. The Hubbell 50 amp rated industrial grade receptical is much thicker and heavier than the 50 amp receptical you get at Home Depot or Lowes. The cost differential is huge. Hubbell recepticals were going for $100+ last I looked, while the Home Depot 50 amp was $10 or so. Bryant seems to make a robust receptical that is a bit cheaper than the Hubbell, but I am not that familiar with it.
If you are working with large wire, you may need to use lugs and a lug tool for attaching the line wire to the charger. My charger recommended lugs. There are some lugs with a set screw fastening system, but others require a lug sqeezing tool (found at any box store or online). Also, as severaltypesofnerdxabove said, you should also need a calibrated tool (e.g., a torque screwdriver) for tightening any sscrews holding wire down to a specific tighness. These tools can be pricy but will come in handy many times if you work with electrical wire. For instance, breaker set screws should always be torqued to a specific torque setting based on manufacturer specifcations.
Hubbell and Bryant are two different brands offered by the same company, and they offer the same model 9450 high-quality 14-50R under both brands. The Bryant can be found at Zoro for $50 or so these days, and the Hubbell is considerably under $100.
Accurate torque tools needn't be expensive. A beam style torque wrench for about $30 can be quite accurate, and the 1/4" drive ones usually have about the right range. It's not a professional electrician's choice, but only because it's not as quick and easy.
Watch out! The current draft of the 2026 National Electric Code removes the cost advantage of hardwired EVSE, buy adding GFCI and a visible emergency shutoff. See Section 625.54 and Section 625.43(B). The comment period is closed, but there are in person meetings in October on the subject.
MORE EXPENSIVE hardwire EVSE on the way.
The pictured Level 1 charger is an example of an unsafe product: It draws 15 A from a regular NEMA 5-15 receptacle, 25% higher than the maximum 12 A allowed for continuous draw on a standard 15 A circuit. Don't assume that products on Amazon are safe. Buy from a reputable manufacturer and double check claims of safety certification.
Amen....good advice.
There are TONS of non-listed non-tested EVSE available on Amazon. Not a good thing.
Log in or become a member to post a comment.
Sign up Log in